How to correctly calculate the number of radiators. Selection of a heating radiator, calculation of the heat output of a radiator according to available parameters.
During modernization of the heating system, in addition to replacing pipes, radiators are also changed. And today they are from different materials, different shapes and sizes. Equally important, they have different heat dissipations: the amount of heat that can transfer to air. And this is necessarily taken into account when calculating sections of radiators.
The room will be warm if the amount of heat that leaves is compensated. Therefore, in the calculations, the heat loss of the premises is taken (they depend on the climatic zone, on the material of the walls, insulation, window area, etc.). The second parameter is the thermal power of one section. This is the amount of heat that it can produce at maximum system parameters (90 ° C at the input and 70 ° C at the output). This characteristic must be indicated in the passport, it is often present on the package.
We do the calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators with our own hands, we take into account the features of the premises and the heating system
One important point: when making calculations yourself, keep in mind that most manufacturers indicate the maximum figure that they received under ideal conditions. Therefore, make any rounding up. In the case of low-temperature heating (inlet temperature below 85 ° C), they search for heat output for the relevant parameters or recalculate (described below).
Area calculation
This is the simplest technique, allowing you to roughly estimate the number of sections required for heating the room. Based on many calculations, the norms for the average heating power of one square of the area are derived. To take into account the climatic features of the region, two norms were prescribed in SNiP:
- for regions of central Russia, from 60 W to 100 W are needed;
- for areas above 60 °, the heating rate per square meter is 150-200 watts.
Why is the norm given such a large range? In order to be able to take into account the materials of the walls and the degree of insulation. For concrete houses, maximum values \u200b\u200bare taken; for brick houses, average values \u200b\u200bcan be used. For insulated houses - minimal. Another important detail: these standards are calculated for the average ceiling height - not higher than 2.7 meters.

Knowing the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, multiply its rate of heat consumption, the most suitable for your conditions. Get the total heat loss of the room. In the technical data for the selected radiator model, find the thermal power of one section. Divide the total heat loss by power, get their number. It is easy, but to make it clearer, we give an example.
An example of calculating the number of sections of radiators by room area
Corner room 16 m 2, in the middle lane, in a brick house. Install batteries with a thermal power of 140 watts.
For a brick house, we take heat loss in the middle of the range. Since the room is angular, it is better to take a larger value. Let it be 95 watts. Then it turns out that 16 m 2 * 95 W \u003d 1520 W is required for space heating.
Now consider the quantity: 1520 W / 140 W \u003d 10.86 pcs. Round, it turns out 11 pcs. So many radiator sections will need to be installed.
Calculation of heating batteries per area is simple, but far from ideal: the height of the ceilings is not taken into account completely. For non-standard heights, a different technique is used: by volume.
Counting batteries by volume
There are norms in SNiP for heating one cubic meter of premises. They are given for different types of buildings:
- for brick 1 m 3 requires 34 watts of heat;
- for panel - 41 W
This calculation of the radiator sections is similar to the previous one, only now we need not the area, but we take others in volume and norms. We multiply the volume by the norm, the resulting figure is divided by the power of one section of the radiator (aluminum, bimetallic or cast iron).

Formula for calculating the number of sections by volume
Volume calculation example
For example, we calculate how many sections are needed in a room with an area of \u200b\u200b16 m 2 and a ceiling height of 3 meters. The building is made of brick. We take the radiators of the same power: 140 W:
- Find the volume. 16 m 2 * 3 m \u003d 48 m 3
- We consider the required amount of heat (the norm for brick buildings is 34 W). 48 m 3 * 34 W \u003d 1632 W.
- We determine how many sections are needed. 1632 W / 140 W \u003d 11.66 pcs. Round, we get 12 pcs.
Now you know two ways to calculate the number of radiators per room.
Heat dissipation in one section
Today, the range of radiators is large. With the outward similarity of most, thermal performance can vary significantly. They depend on the material from which they are made, on the dimensions, wall thickness, internal section and on how well the design is thought out.
Therefore, to say exactly how many kW is in 1 section of an aluminum (cast-iron bimetallic) radiator can only be said for each model. This data is indicated by the manufacturer. After all, there is a significant difference in size: some of them are tall and narrow, while others are low and deep. Power sections of the same height of the same manufacturer, but different models, may vary by 15-25 watts (see the table below STYLE 500 and STYLE PLUS 500). Even more noticeable differences may be from different manufacturers.

Nevertheless, for a preliminary assessment of how many sections of batteries are needed for space heating, the average values \u200b\u200bof thermal power for each type of radiator were derived. They can be used for approximate calculations (data for batteries with a center distance of 50 cm are given):
- Bimetal - one section emits 185 W (0.185 kW).
- Aluminum - 190 W (0.19 kW).
- Cast iron - 120 W (0.120 kW).
More precisely, how many kW in one section of a bimetallic, aluminum or cast-iron radiator can you when you select a model and decide on the dimensions. There may be a big difference in cast iron batteries. They are with thin or thick walls, due to which their thermal power changes significantly. Above are the average values \u200b\u200bfor batteries of a familiar shape (accordion) and close to it. Retro-style radiators have significantly lower thermal output.

These are the technical specifications of cast-iron radiators of the Turkish company Demir Dokum. The difference is more than substantial. She can be even bigger
Based on these values \u200b\u200band average norms in SNiP, the average number of radiator sections per 1 m 2 was derived:
- bimetallic section heats 1.8 m 2;
- aluminum - 1.9-2.0 m 2;
- cast iron - 1.4-1.5 m 2;
- bimetallic 16 m 2 / 1.8 m 2 \u003d 8.88 units, rounded - 9 units.
- aluminum 16 m 2/2 m 2 \u003d 8 pcs.
- cast-iron 16 m 2 / 1.4 m 2 \u003d 11.4 pcs, rounded - 12 pcs.
These calculations are only approximate. According to them, you can approximately estimate the cost of purchasing heating appliances. You can accurately calculate the number of radiators per room by selecting a model, and then recounting the amount depending on what temperature of the coolant in your system.
Calculation of sections of radiators depending on actual conditions
Once again, we draw your attention to the fact that the thermal power of one section of the battery is indicated for ideal conditions. The battery will produce so much heat if its coolant has a temperature of + 90 ° C at the inlet, + 70 ° C at the outlet, and + 20 ° C is maintained in the room. That is, the temperature head of the system (also called the "delta system") will be 70 ° C. What to do if your system has a temperature above + 70 ° C at the input? or do you need a room temperature of + 23 ° C? Recalculate declared capacity.
To do this, you need to calculate the temperature head of your heating system. For example, at the supply you have + 70 ° C, at the outlet 60 ° C, and in the room you need a temperature of + 23 ° C. We find the delta of your system: this is the arithmetic average of the temperatures at the inlet and outlet, minus the temperature in the room.

For our case, it turns out: (70 ° C + 60 ° C) / 2 - 23 ° C \u003d 42 ° C. Delta for such conditions is 42 ° C. Next, we find this value in the conversion table (located below) and the declared power is multiplied by this coefficient. We learn the power that this section can give out for your conditions.
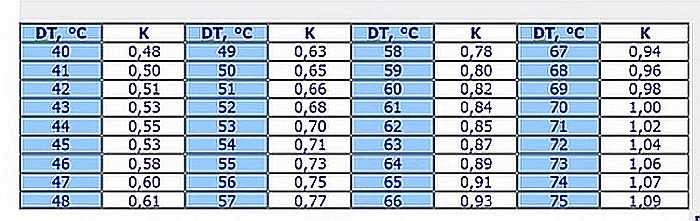
We find in the columns, tinted in blue, a line with a delta of 42 ° C. It corresponds to a coefficient of 0.51. Now we calculate the thermal power of 1 section of the radiator for our case. For example, the declared power of 185 W, applying the found coefficient, we obtain: 185 W * 0.51 \u003d 94.35 W. Almost half as much. It is this power that needs to be substituted when doing the calculation of sections of radiators. Only taking into account individual parameters in the room will be warm.
Calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators
Heating radiators - this is the most common heating device that is installed in residential, public and industrial premises. It is a hollow inside the elements filled with coolant. Through them, thermal energy enters the room for heating. When choosing radiators, you must first pay attention to two technical indicators. This is the power of the device and the coolant pressure it can withstand. But in order to finally determine the temperature regime of the room, it is necessary to conduct an accurate calculation of heating radiators.
This includes not only the number of devices themselves and their sections, but also the material from which they are made. The modern market for heating equipment offers a huge range of batteries with different technical characteristics. The main thing you need to know is the capabilities of one section of the battery, namely, its ability to release the maximum amount of thermal energy. This indicator will form the basis of the ongoing.
We will calculate
Knowing that 100 watts of heat is needed per 1 square meter of room space, you can easily calculate the number of radiators needed. Therefore, first you need to accurately determine the area of \u200b\u200bthe room where the batteries will be installed.
The height of the ceilings, as well as the number of doors and windows, are necessarily taken into account - after all, these are openings through which heat evaporates most quickly. Therefore, the material from which the doors and windows are made is also taken into account.
Now the lowest temperature in your area and the temperature of the coolant at the same time are determined. All the nuances are calculated using the coefficients that are listed in SNiP. Given these factors, you can calculate the heating power.
A quick calculation is made by simply multiplying the room area by 100 watts. But it will not be accurate. For correction and coefficients are used.
Power Correction Factors
There are two of them: decrease and increase.
Power reduction factors are used as follows:
- If plastic multi-chamber double-glazed windows are installed on the windows, the indicator is multiplied by 0.2.
- If the ceiling height is less than the standard (3 m), then a reduction factor is applied. It is defined as the ratio of the actual height to the standard. Example - the ceiling height is 2.7 m. Therefore, the coefficient is calculated by the formula: 2.7 / 3 \u003d 0.9.
- If the heating boiler operates with increased power, then every 10 degrees of the heat energy generated by it reduces the power of heating radiators by 15%.
Power increase factors are taken into account in the following situations:
- If the ceiling height is above the standard size, then the coefficient is calculated using the same formula.
- If the apartment is angular, then a factor of 1.8 is used to increase the power of heating appliances.
- If the radiators have a lower connection, then 8% is added to the calculated value.
- If the boiler lowers the temperature of the coolant on the coldest days, then for every 10 degrees of decrease, an increase in battery power by 17% is necessary.
- If sometimes the temperature on the street reaches critical levels, then you will have to increase the heating power by 2 times.
We determine the number of sections of one radiator

Equipment sections
Experts offer several options for calculating the number of heating radiators and their sections.
The first is the so-called ordinary method. He is the easiest. Usually in the passport or quality certificate, which is issued as an accompanying document for each product, the technical parameters are set. Here you can find information about how much power one section of heating radiators has.
For example, it is equal to 200 watts. The power required to heat the room is calculated, taking into account the decreasing and increasing coefficients. Suppose that it is 2400 watts.
Now purely mathematical calculations are made: 2400/200 \u003d 12. This is the number of sections that must be installed in this room. You can use one 12-cell battery or two 6-cell.
The second option - the calculation is made taking into account the heating ability of one section for a certain amount of space. For this, the total volume of the room is calculated and divided by the volume heating index of the section.

Coloring of heating equipment
The third is an approximate calculation used by masters, based on their personal experience. All radiators are almost the same size. There are differences, but minor. So it was noticed that with a ceiling height of 2.7 meters, one section can heat an area equal to 1.8 square meters.
For example, a room has an area of \u200b\u200b25 m2. We carry out the calculation: 25 / 1.8 \u003d 13.8. That is, 14 sections will need to be installed.
As you can see, calculating heating batteries is not so difficult. It is important to consider all the parameters that affect the system itself. True, sometimes it can be difficult to do.
Therefore, the advice: involve professionals in this process - after all, a small mistake or a minimal flaw can lead to an undesirable situation. You will simply not be comfortable in an apartment or a house in winter - when the air temperature does not reach room temperature.
Related posts
In the matter of maintaining the optimum temperature in the house, the main place is taken by the radiator.
The choice is simply amazing: bimetallic, aluminum, steel of various sizes.
There is nothing worse than a wrongly calculated required heat output in a room. In winter, such a mistake can be very expensive.
The thermal calculation of heating radiators is suitable for bimetallic, aluminum, steel and cast iron radiators. Specialists distinguish three ways, each of which is based on certain indicators.
There are three methods that are based on general principles:
- the standard power value of one section can vary from 120 to 220 W, so the average value is taken
- to correct errors in the calculations when buying a radiator, you should lay a 20% reserve
Now we turn directly to the methods themselves.
Method One - Standard
Based on building rules, for high-quality heating of one square meter, 100 watts of radiator power is required. Let's do the calculations.
Let's say the area of \u200b\u200bthe room is 30 m², we take the power of one section equal to 180 watts, then 30 * 100/180 \u003d 16.6. We round the value up and get that for a room of 30 square meters you need 17 sections of a heating radiator.
However, if the room is angular, then the resulting value should be multiplied by a factor of 1.2. In this case, the number of required sections of radiators will be equal to 20
Method Two - Approximate
This method differs from the previous one in that it is based not only on the area of \u200b\u200bthe room, but also on its height. Please note that the method works only for medium and high power devices.
At low power (50 watts or less), such calculations will be ineffective due to too much error.
So, if you take into account that the average height of the room is 2.5 meters (the standard ceiling height of most apartments), then one section of a standard radiator can heat an area of \u200b\u200b1.8 m².
The calculation of the sections for a room of 30 "squares" will be as follows: 30 / 1.8 \u003d 16. Again we round up and we get that for heating this room you need 17 sections of a radiator.
Method Three - Volumetric
As the name implies, the calculations in this method are based on the volume of the room.
It is conditionally accepted that for heating 5 cubic meters of a room, 1 section with a power of 200 watts is needed. With a length of 6 m, a width of 5 and a height of 2.5 m, the formula for the calculation will be as follows: (6 * 5 * 2.5) / 5 \u003d 15. Therefore, for a room with such parameters, 15 sections of a heating radiator with a power of 200 watts each are needed.
If the radiator is planned to be located in a deep open niche, then the number of sections should be increased by 5%.
If the radiator is planned to be completely covered with a panel, then an increase should be made by 15%. Otherwise, it will be impossible to achieve optimal heat transfer.
Alternative method for calculating the power of heating radiators
 The calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators is far from the only way to properly organize the heating of the room.
The calculation of the number of sections of heating radiators is far from the only way to properly organize the heating of the room.
We calculate the volume of the proposed room with an area of \u200b\u200b30 square meters. m and a height of 2.5 m:
30 x 2.5 \u003d 75 cubic meters
Now you need to determine the climate.
For the territory of the European part of Russia, as well as Belarus and Ukraine, the standard is 41 watts of heat capacity per cubic meter of space.
To determine the required power, we multiply the volume of the room by the standard:
75 x 41 \u003d 3075 W
We round the obtained value upwards - 3100 watts. For those people who live in very cold winters, this figure can be increased by 20%:
3100 x 1.2 \u003d 3720 watts.
Arriving at the store and specifying the power of the heating radiator, you can calculate how many sections of the radiator will be required to maintain a comfortable temperature even in the harshest winter.
Calculation of the number of radiators

The calculation method is an excerpt from the previous paragraphs of the article.
After you calculate the required power for heating the room and the number of sections of the radiator, you come to the store.
If the number of sections turned out to be impressive (this happens in rooms with a large area), then it will be reasonable to purchase not one, but several radiators.
This scheme is also applicable to those conditions when the power of one radiator is lower than necessary.
But there is another quick way to calculate the number of radiators. If your room was old with a height of about 60 cm, and in winter you felt comfortable in this room, then count the number of sections.
Multiply the resulting figure by 150 watts - this will be the necessary power of the new radiators.
At the moment, you can send an application for the calculation of heating to
Email: [email protected]
The necessary data for the calculation:
|
|
The calculation is made within 1-2 days, tk. loading of our engineers is very big!
Calculation results and tips for building heating are sent in response to a request to your Email!
We make the calculation completely free! In exchange, please tell your friends about us on social networks!
Thank!
Get a professional calculation of heating radiators for FREE!Send an application for the calculation of heating radiators by professionals, the calculation is absolutely FREE!
You are required to inform the parameters of your apartment:
- Number of sq / m.
- The number of floors in the house
- Your floor
- Corner apartment? (Well no)
SEND APPLICATION
Payment aluminum radiators - This is a very important task that our online calculator will do just fine. Here you can produce high quality and accurate enough calculation of sections of aluminum heating radiators required to heat the area you need.
Video with an example of calculating sections of an aluminum radiator
In this case, we consider only calculation of the number of aluminum radiators since they have recently gained more and more popularity among the population, their indisputable advantages are high heat dissipation, quick heating and convenient thermoregulation, ease of installation due to their light weight and low cost compared to other types of heating radiators.
For exact calculation of aluminum heating radiators you need to fill in all the additional parameters, do not neglect them!
Calculation of the number of aluminum radiators It is carried out according to a formula similar to the calculation of other radiators, here all the salt in the power of one section, for calculation at non-standard power, you can divide the obtained value “Required power” by the power of one section, which will give you the desired number of sections of aluminum heating radiators for your living room .
How to calculate heating radiators by area? Owners of private houses and city apartments are asking this question. Many are afraid to make mistakes during installation, as a result of which the room will be too cold or hot.
Why careful calculation is necessary:
- The temperature in the room and the comfort of the residents depend on this.
- Proper design of the system will optimize the additional costs of installing equipment.
- The cost of paying for resources is slightly reduced.
- Real efficiency and power are increasing.
Radiators of different sizes
Important! Calculations can be done in several ways, depending on the characteristics of the room and related parameters. But you need to consider many additional factors that can affect the construction of the system.
- Corner rooms have street walls. This fact slightly increases the heat loss of the room.
- The degree of cooling depends on the number of windows; they give off heat faster than walls.
- When using steam carriers, the heat transfer increases significantly, this must be taken into account in the calculation.
- For rooms with high ceilings of more than three meters, the calculation of the area cannot be applied, it is necessary to take into account the volume.
- An important factor is the material that was used to make the heater. Each metal has a certain degree of heat transfer, which affects its effectiveness.
- When moving the medium in the heating system from top to bottom, the heating efficiency increases by 20 percent.
- The presence of thermal insulation in the walls significantly reduces associated losses. This also applies to modern double-glazed windows, they retain heat much better.
- If the pipes are connected only on one side, then putting more than 10 sections into the battery does not make sense.
- When using a ventilation system, heat loss increases, it will be necessary to increase power.
- Do not forget about the minimum winter temperatures in the region, they directly affect the power of the heating system.

Comparison table of heating appliances
If you take into account the related parameters when building the system, you can create an efficient heating system. It will provide space heating regardless of the temperature outside the window.
Common mistakes
- The use of a large number of sections in circular devices. The coolant cannot get into all parts, the real radiator efficiency is reduced.
- Not enough devices or sections. The system is unable to provide proper heating; additional adjustments will have to be made.
- Too many devices, but this problem can be solved by installing limiters to control the amount of incoming coolant.
- Incorrect odds, such errors lead to serious miscalculations.

One-way battery should not have more than 10 sections
Any errors can lead to serious consequences. Try to carefully select the coefficients for the room and take into account the data obtained when creating the system.
Important! Remember that all calculations are approximate, because it is simply impossible to take into account the whole complex of parameters. But using the recommended formulas, you can create effective heating.
Calculation taking into account the area
According to current standards, per 1 square. The meter should account for 100 watts of power. The calculation must be performed as follows:
- Initially, you should find out the area of \u200b\u200ba room by measuring or from a technical passport.
- The area must be multiplied by 100 watts. If it is equal to 30 squares, then the power will be 3000 watts.
- Choose a radiator of a suitable manufacturer, specify the power of one section. Suppose that it is equal to 150 watts, therefore, it is necessary to divide 3000 into 150, we get 20 sections.
It is necessary not only to understand how to calculate the size of the heating radiator according to this formula, but also to make additional adjustments. If the room is angular and has a balcony, but the data obtained should be increased by 20 percent. Another 20 percent must be added during installation in a niche or behind a screen, with this arrangement, real efficiency decreases. The obtained result indicates the number of sections, they should be distributed to several heating devices.
By volume
According to current standards, 41 watts of power should be per cubic meter. But this is a parameter for prefabricated houses, for apartments in modern buildings and with plastic windows it can be reduced to 34 watts. The calculation must be carried out according to the following scheme:
- You need to know the area of \u200b\u200bthe room and the height of the ceilings, for example, 15 square meters. m. and 3 meters. We multiply these indicators, we get 45 m 3.
- We multiply the volume by the normalized power value, that is, 45 * 41 \u003d 1845.
- We find out the power of the radiator section from the manufacturer of interest, divide by it the result obtained earlier. If it is equal to 150 watts, then 1845/150 \u003d 12.3. This value should be rounded, we get 12 sections.

Cast iron and bimetal radiators similar in heat transfer
More accurate area calculation method
But how to calculate the number of radiators with maximum accuracy? Past methods allow you to get an approximate value and take into account only the main factors. But if you want to get rid of many shortcomings and take into account heat loss, then you should use another option.
The main advantages of the method:
- Consideration of the features of materials and double-glazed windows, the degree of thermal insulation of the room.
- The calculations reflect the design of the house and the location of the room.
- You can learn the minimum temperature and other factors.
The formula for calculating the power of the system: CT \u003d 100W / sq.m. * P * K1 * K2 * K3 * K4 * K5 * K6 * K7.
P is the area of \u200b\u200bthe premises in square meters; for K1 is taken the glazing of window openings; K2 - thermal insulation of walls in the room; K3 takes into account the ratio of the area of \u200b\u200bthe windows and the floor; K4 - the average temperature in the cold season; K5 reflects the number of street walls; K6 - location above a specific type of room; K7 - ceiling height.
When using this method, you can take into account all the factors affecting the cooling of the room and the associated losses. You need to multiply the basic parameters, you can get accurate data. The result should be divided by the power of one section in the radiator, after you find out the required value.

